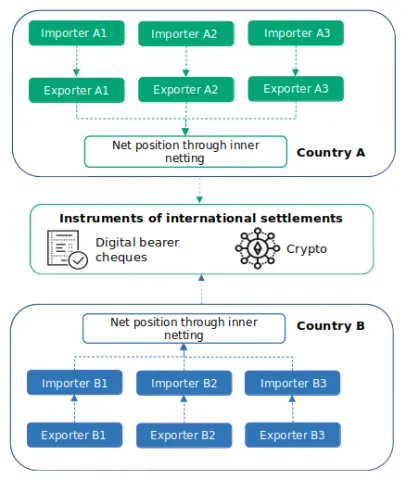
Cross-border payments based on a distributed ledger
Web3 Tech helps to reorganizing money flow to minimize utility of standard channels between countries via blockchain technologies.
Blockchain platform usage options:
Digital bearer cheques (Digital Financial Asset)
- Digital bearer cheques live cycle management (tokens backed by currency at account of certain financial organizations).
- Cheque issuance is verified through the bank’s blockchain signature.
- One cheque equals one unit of the fiat currency
- Cheques exchange at the trading platform (either decentralized or centralized)
Domestic clearing for exporters and importers
Crypto payments
Paragraph
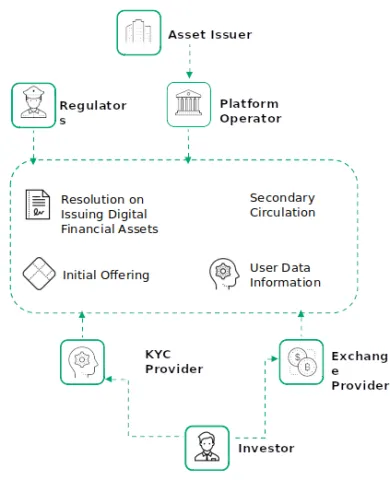
DFA Common Description
How it works:
- The platform operator, exchange providers and regulators install their distributed ledger nodes.
- The asset issuer works out resolution on issuing digital financial assets and approves all its conditions with an authorized network participant.
- The information about new digital financial assets becomes available to the investors, who operate at the platform with the help of exchange providers. The investors can take part in the initial offering.
- Successful initial offering results in digital financial asset emission.
- Investors can buy and sell digital financial assets during their secondary circulation. Exchange providers process and match the buy and sell orders here.
- Digital financial assets can represent any other assets, such as securities, bonds, derivatives and others. The distributed ledger enables to automate digital assets, e.g., paying coupon bonds.
- KYC procedure for investors can be done by either an exchange or a stand-alone provider. For the regulators, the platform can form reports about operations with digital financial assets.
Our advantages:
- Investors get innovative financial instruments with a large set of basic assets available.
- Digital financial assets can be automated at their tech level.
- Blockchain offers native instruments for transaction recording, client accounting, and double-spending prevention.
Bullet text
Interest-sensitive DFA
Paragraph
- Bonds, financial claims, and the like
- The interest rate is fixed and stated in the resolution on issuing
- DFA can either have an underlying asset or not
- The circulation is not limited in time
- The fund transfer and the following payment from the issuer’s checking account to the investors are provided with the help of CBS
- Third-party data sources (oracles) can be connected to import the actual prices
- Total value of payments and interest/main debt are calculated according to the platform operator’s schedule
- Splitting payments to different investors can be provided by the platform
Bullet text
Interest-free DFA
Paragraph
- Securities, zero-coupon bonds, tokenized (hybrid) assets, and the like
- DFA can either have an underlying asset or not
- The circulation is not limited in time
- Third-party data sources (oracles) can be connected to import the actual prices
Bullet text
Other DFA (customized box solution)
Paragraph
- The platform enables creating DFA with customized payments, price estimation and circulation.
- The platform users can create their own DFA with custom mechanics.
- Sukuk, often referred to as Islamic bonds. They represent proportionate ownership in tangible assets, projects, or services. Sukuk holders receive a share of the profits generated by the underlying assets. Key Feature: Asset-backed investment tool adhering to Islamic finance principles.
- Murabaha is a cost-plus-profit arrangement where the bank purchases an asset on behalf of the client and then sells it to the client at a markup. This is a common mode of Islamic financing for trade and commodity transactions. Key Feature: Transparent cost structure with the seller's profit explicitly disclosed.
- Mudarabah is a profit-sharing partnership, where one party provides the capital (Rab ul Mal) and another provides the expertise (Mudarib). Profits are shared based on a pre-agreed ratio, but losses are borne by the capital provider. Key Feature: Risk and profit-sharing partnership.
- Musharakah is a form of partnership in Islamic finance where two or more parties collaborate to contribute capital for a business venture. All partners share in the profits or losses based on a pre-agreed ratio. Unlike a conventional loan, Musharakah involves a shared risk and reward mechanism. Key Feature: Joint venture partnership emphasizing shared ownership and responsibility.
- Takaful is an insurance concept that operates on the principles of mutual cooperation and shared responsibility. Participants contribute money into a pool to guarantee each other against loss or damage. In the event of a claim, funds from the pool are utilized to compensate the affected participants. Key Feature: Cooperative risk-sharing model adhering to Islamic principles.